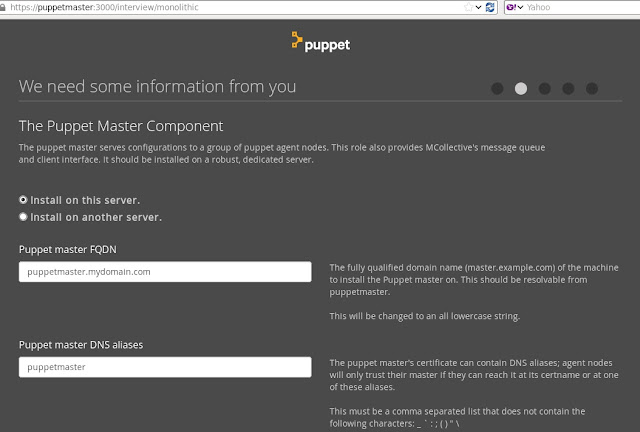
How to add 3 new external hdds and create LVM on it.
steps required to configure LVM include:
- Creating physical volumes from the hard drives.
- Creating volume groups from the physical volumes.
- Creating logical volumes from the volume groups and assign the logical volumes mount points
In this case external hdds connected to the server as /dev/sdc, /dev/sdd, /dev/sde
[ The command fdisk -l will show the hdds connected to the server ]
1. Create a partition on the hdd and change file system to 8e (LVM )
Note:- This is a destructive process, and make sure that any data in the hdd is backed up before proceeding.
a) fdisk /dev/sdc
b) enter "n" to create partition,
enter "1" to create primary partition
select start and end as default (just press enter at both prompts )
c) enter "t" to change the file system type and enter '8e' for LVM
d) enter "w" to save the changes
e) enter "q" to exit
2) Create Physical volume
3) Create Volume group from the Physical volumes create
Here I am creating a Volume group "DB_TEST_EXTERNAL"
4) Create Logical Volume from the Volume group
Here I am creating a Logical Volume named "LV_DATA"

5) Create filesystem on the share
mkfs.ext3 /dev/DB_TEST_EXTERNAL/LV_DATA